Organic Chemistry 1
General Outline
Organic Chemistry 1:
Atoms and Orbitals
- Trends in the Periodic Table
- Electronegativity
- Atomic Radius/Polarizability
Acids and Bases in Organic Chemistry
- Definitions
- pKa
- Inductive Effects
- Resonance Effects
- Introduction to Bonds and Molecules
- Hybridization
- Types of Bonds
- Lewis Structures
- Resonance Structures
- Ways of Representing Molecules
- Condensed Formula
- Structural Formula
- Bond-Angle Formula
- Constitutional Isomerism
- Special Topic: The Molecular Model Kit
- Formal Charge
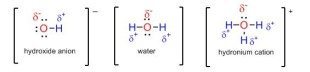
Conformational Isomerism
- Other Representations
- Newman Projections
- Cyclohexane Conformers
- Fischer Projections
IUPAC system of Nomenclature
- Alkanes
- Cycloalkanes
- Alkenes
- Alkynes
- Alkyl Halides
- Alcohols
- Ethers
- Other Functional Groups
Reactions of Alkenes: The Electrophilic Addition Reaction (AdE3)
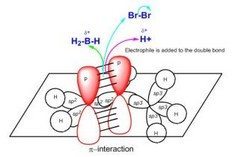
- Reaction Coordinate Diagrams and the Potential Energy Surface
- Transition States vs. Intermediates
- Free Energy (G) & Enthalpy (H)
- Carbenium ions/Carbocations
- Hyperconjugation
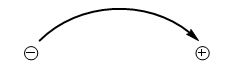
Introduction to Mechanism: The Arrow-Pushing Formalism
- Regiochemistry
- Markovnikov's Rule (Anti-Markovnikov Regiochemistry)
Relative Stereochemistry
- Syn vs Anti Addition
Thermodynamics and Kinetics
- Reactions of Dienes
- Radical Reactions
- Alkane Halogenation
- Initiation, Propagation, Termination
Chirality and Stereochemistry
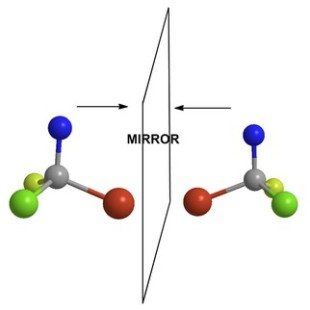
- Configurational Isomerism
- Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (C-I-P) Rules & Determination of Absolute Configuration
- Enantiomers
- Diastereomers
- Meso Compounds
- Optical Activity
- Enantiomeric Excess
- Racemic vs. Scalemic
- Axial chirality, Helical chirality,
- Prochirality and the Concepts of Homo- and Heterotopicity
- Alkynes: Introduction to Synthesis—C-C bond formation
- pKa of sp carbon and Acetylides
- Addition Reactions of Alkynes
Reaction Pathways at sp3 Carbons
- (SN1/SN2)
- Bimolecular and Unimolecular Substitution at sp3 Carbon.
- Relative rates of reaction.
Important oxygen-containing functional groups, their synthesis and typical reactivity.
- Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
- Pseudo Halides and Alcohol Activation
- (E1/E2)
- Bimolecular and unimolecular elimination mechanisms.
- Zaitzev's Rule vs Hoffman's Rule.
Introduction to Retrosynthetic Analysis
- Bond disconnection and planning
Structural Elucidation: Analysis and Identification of Organic Compounds
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
- Electron Impact Mass Spectrometry
- Molecular Ion peak vs. the Base Peak
- Isotopes and their Consequences in MS
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
- Hookes' Law
- Absorption Spectroscopy
- Bonds and their Stretch, Bend, and Wag Peaks.
- Overtones and the Fingerprint Region.
lH and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
- Nuclear Spin States
- Free induction decay
- Fourier transformation
- Interpretation of NMR spectra
*Other Analytical Methods
(when taken with Organic Chemistry Laboratory)
UV-Vis spectroscopy
- The Woodward Rules
Polarimetry
- [α°]D
Gas Chromatography
- Retention Time
Thin-layer Chromatography
- How can you tell when a reaction has gone to completion?
Column Chromatography
- How do you purify side products from the desired product?

Ready to conquer organic chemistry with confidence? Explore our services and resources now to start your journey towards success! Join our community of learners and unlock your full potential in organic chemistry. Let's embark on this exciting journey together. Get started today!
Read More